AMSOIL products slow the rate of oxidation via Antioxidants in Marine Oil
Let me tell you something. While we breathe oxygen to live, oxygen is bad for lubricants. Oxidation increases the rate at which a lubricant breaks down and becomes ineffective. Boat engines constantly operate under severe conditions that increase the risk of oil oxidation, which leads to chemical breakdown and sludge. Examining the oil components will open your eyes to what’s going on.
Oxidation of your Oil
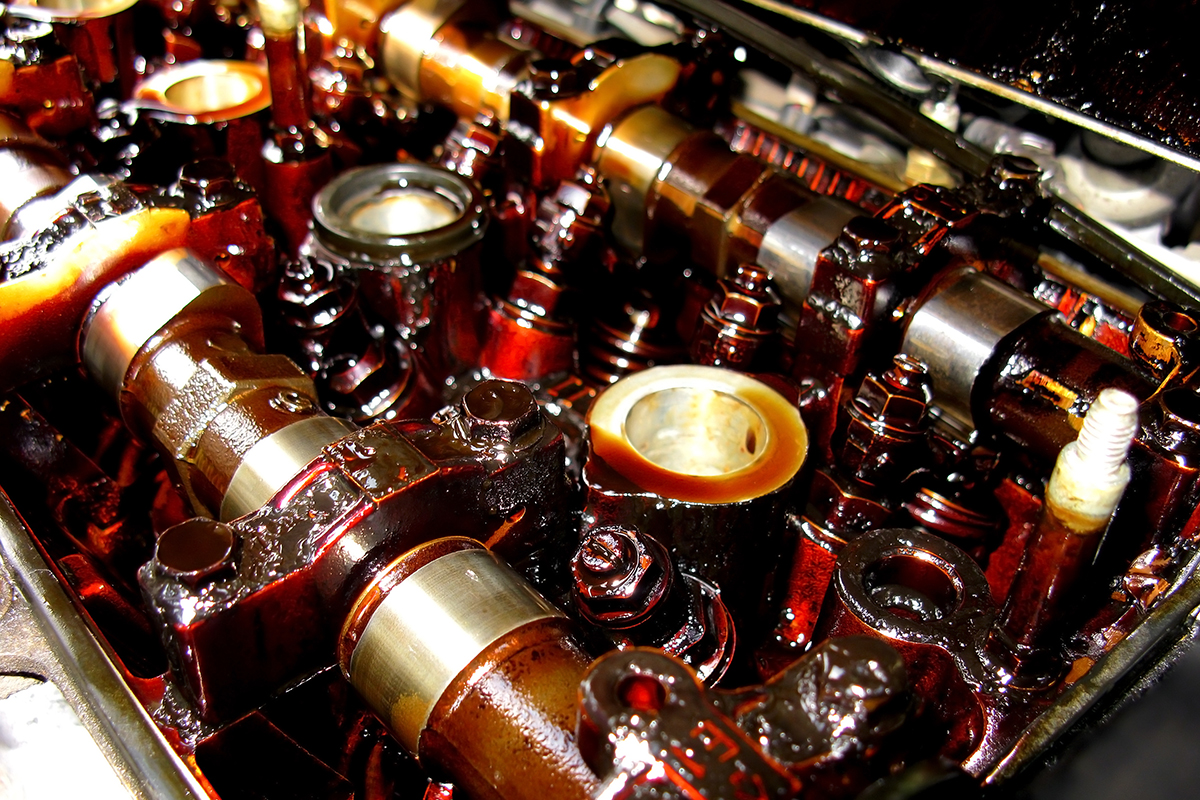
Oxidation causes oil degradation that leads to oil thickening and the formation of sludge, corrosive acids and varnish. As oil oxidizes, it forms deposits that increase its viscosity and adhere to component surfaces, reducing engine efficiency and increasing component wear. Oxidation can also deplete the additive content of motor oil, leaving both the oil and the engine susceptible to the effects of degraded oil. The effects of oxidation are accelerated as temperatures increase.
Also for those who want to run a thicker (higher viscosity oil) because it’s hot out or the conditions are hot will also increase temperature which directly increases oxidation. We only recommend increasing oil viscosity if it’s one listed by the manufacturer.
Sludge
Sludge is a thick residue typically composed of oxidation and combustion byproducts. It can also be formed by contaminants like wear particles, water, fuel and coolant, which are often acidic and insoluble in the motor oil. These contaminants can agglomerate and deposit on surfaces inside the engine. The polar nature of sludge pulls other contaminants out of suspension and bonds with them, accelerating the sludge-formation process. As sludge deposits rapidly expand, they start causing performance issues.
Sludge can form anywhere, but it typically starts on non-moving engine components, including the tops of cylinder heads, valve covers and oil pans. Marine engines are particularly susceptible to sludge and deposits as they produce extreme stress on engine oil due to water and fuel dilution and higher temperatures, which all accelerate the byproduct creation.
Antioxidants
Better oxidative stability slows the rate of oil oxidation to help prolong the oil’s life, especially at higher temperatures. Antioxidant additives prevent oil from reacting with oxygen and improve its oxidation resistance. Antioxidants decompose peroxides and terminate free-radical reactions to slow oxidation and extend lubricant life.
Base Oil
The base oil performance properties provide most of an engine oil’s oxidation resistance. Synthetic oil molecules are saturated with hydrogen molecules, which helps prevent oxygen molecules from attaching and initiating the oxidation process. Synthetic base oils are also contaminant-free, which further improves their inherent antioxidant properties.
AMSOIL Advantage
AMSOIL Marine Engine Oil is engineered with high-quality synthetic base oils and a robust antioxidant additive package that increases the oxidative stability to inhibit sludge formation and help the oil last longer in severe-service marine applications. It also contains premium detergents and dispersants that helps neutralize the sludge-forming acids and keep solid contaminants in suspension to be removed at the next oil change.
Quickly find the right products for your marine engine using our convenient lookup guides. And be sure to save money by buying locally here in our Omaha store at 4211 S. 84th St.